Top Important Computer Vision Papers for the Week from 18/9 to 24/9
Stay Relevant to Recent Computer Vision Research
On a weekly basis, several top-tier academic conferences and journals showcased innovative research in computer vision, presenting exciting breakthroughs in various subfields such as image recognition, vision model optimization, generative adversarial networks (GANs), image segmentation, video analysis, and more.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the most significant papers published in the third week of September 2023, highlighting the latest research and advancements in computer vision. Whether you’re a researcher, practitioner, or enthusiast, this article will provide valuable insights into the state-of-the-art techniques and tools in computer vision.
Table of contents:
Image Recognition
Image Generation
3D Computer Vision
Are you looking to start a career in data science and AI and need to learn how? I offer data science mentoring sessions and long-term career mentoring:
Mentoring sessions: https://lnkd.in/dXeg3KPW
Long-term mentoring: https://lnkd.in/dtdUYBrM
All the resources and tools you need to teach yourself Data Science for free!
The best interactive roadmaps for Data Science roles. With links to free learning resources. Start here: https://aigents.co/learn/roadmaps/intro
The search engine for Data Science learning recourses. 100K handpicked articles and tutorials. With GPT-powered summaries and explanations. https://aigents.co/learn
Teach yourself Data Science with the help of an AI tutor (powered by GPT-4). https://community.aigents.co/spaces/10362739/
1. Image Recognition
1.1. Replacing softmax with ReLU in Vision Transformers
Previous research observed accuracy degradation when replacing the attention softmax with a point-wise activation such as ReLU. In the context of vision transformers, we find that this degradation is mitigated when dividing by sequence length. Our experiments training small to large vision transformers on ImageNet-21k indicate that ReLU-attention can approach or match the performance of softmax-attention in terms of scaling behavior as a function of computing.
1.2. RMT: Retentive Networks Meet Vision Transformers
Transformer first appears in the field of natural language processing and is later migrated to the computer vision domain, where it demonstrates excellent performance in vision tasks. However, recently, Retentive Network (RetNet) has emerged as an architecture with the potential to replace Transformer, attracting widespread attention in the NLP community. Therefore, we raise the question of whether transferring RetNet’s idea to vision can also bring outstanding performance to vision tasks.
To address this, we combine RetNet and Transformer to propose RMT. Inspired by RetNet, RMT introduces explicit decay into the vision backbone, bringing prior knowledge related to spatial distances to the vision model. This distance-related spatial prior allows for explicit control of the range of tokens that each token can attend to. Additionally, to reduce the computational cost of global modeling, we decompose this modeling process along the two coordinate axes of the image.
Abundant experiments have demonstrated that our RMT exhibits exceptional performance across various computer vision tasks. For example, RMT achieves 84.1% Top1-acc on ImageNet-1k using merely 4.5G FLOPs. To the best of our knowledge, among all models, RMT achieves the highest Top1-acc when models are of similar size and trained with the same strategy. Moreover, RMT significantly outperforms existing vision backbones in downstream tasks such as object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation. Our work is still in progress.
2. Image Generation
2.1. Viewpoint Textual Inversion: Unleashing Novel View Synthesis with Pretrained 2D Diffusion Models
Text-to-image diffusion models understand spatial relationships between objects, but do they represent the true 3D structure of the world from only 2D supervision? We demonstrate that yes, 3D knowledge is encoded in 2D image diffusion models like Stable Diffusion, and we show that this structure can be exploited for 3D vision tasks. Our method, Viewpoint Neural Textual Inversion (ViewNeTI), controls the 3D viewpoint of objects in generated images from frozen diffusion models. We train a small neural mapper to take camera viewpoint parameters and predict text encoder latents; the latents then condition the diffusion generation process to produce images with the desired camera viewpoint. ViewNeTI naturally addresses Novel View Synthesis (NVS). By leveraging the frozen diffusion model as a prior, we can solve NVS with very few input views; we can even do single-view novel view synthesis. Our single-view NVS predictions have good semantic details and photorealism compared to prior methods. Our approach is well suited for modeling the uncertainty inherent in sparse 3D vision problems because it can efficiently generate diverse samples. Our view-control mechanism is general, and can even change the camera view in images generated by user-defined prompts.
2.2. FoleyGen: Visually-Guided Audio Generation
Recent advancements in audio generation have been spurred by the evolution of large-scale deep-learning models and expansive datasets. However, the task of video-to-audio (V2A) generation continues to be a challenge, principally because of the intricate relationship between the high-dimensional visual and auditory data, and the challenges associated with temporal synchronization. In this study, we introduce FoleyGen, an open-domain V2A generation system built on a language modeling paradigm. FoleyGen leverages an off-the-shelf neural audio codec for bidirectional conversion between waveforms and discrete tokens.
The generation of audio tokens is facilitated by a single Transformer model, which is conditioned on visual features extracted from a visual encoder. A prevalent problem in V2A generation is the misalignment of generated audio with the visible actions in the video. To address this, we explore three novel visual attention mechanisms. We further undertake an exhaustive evaluation of multiple visual encoders, each pretrained on either single-modal or multi-modal tasks. The experimental results on the VGGSound dataset show that our proposed FoleyGen outperforms previous systems across all objective metrics and human evaluations.
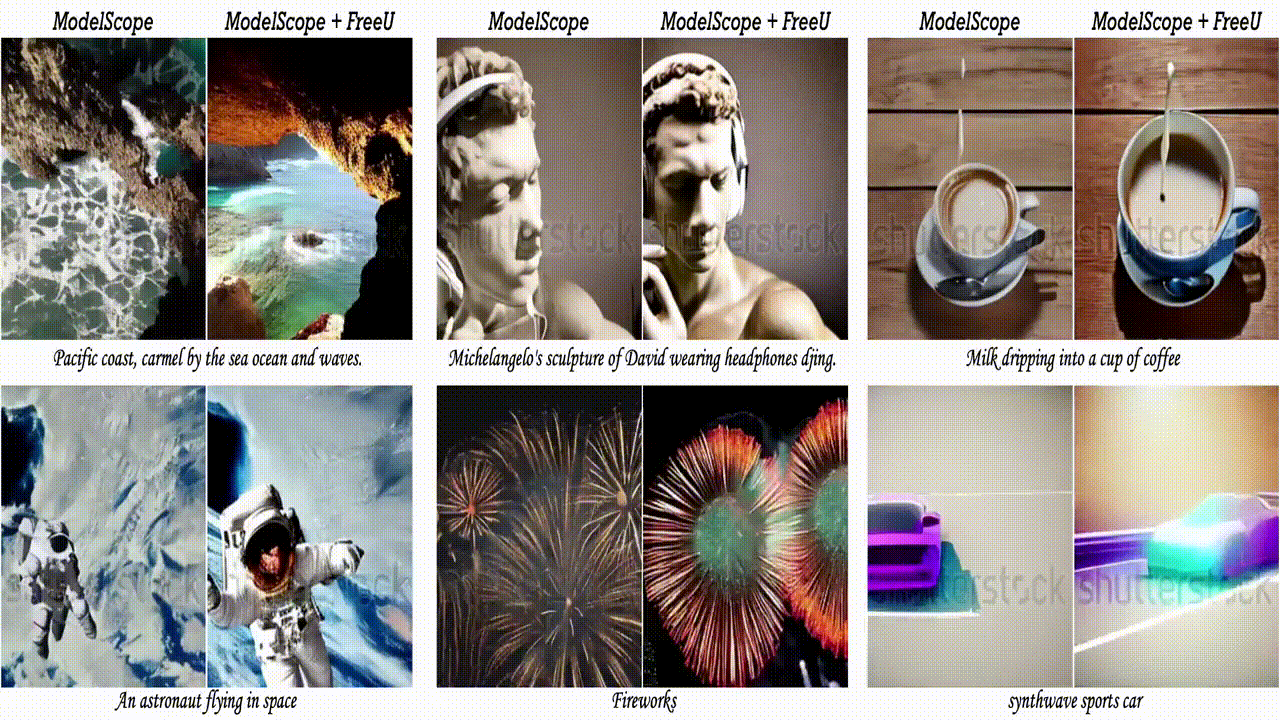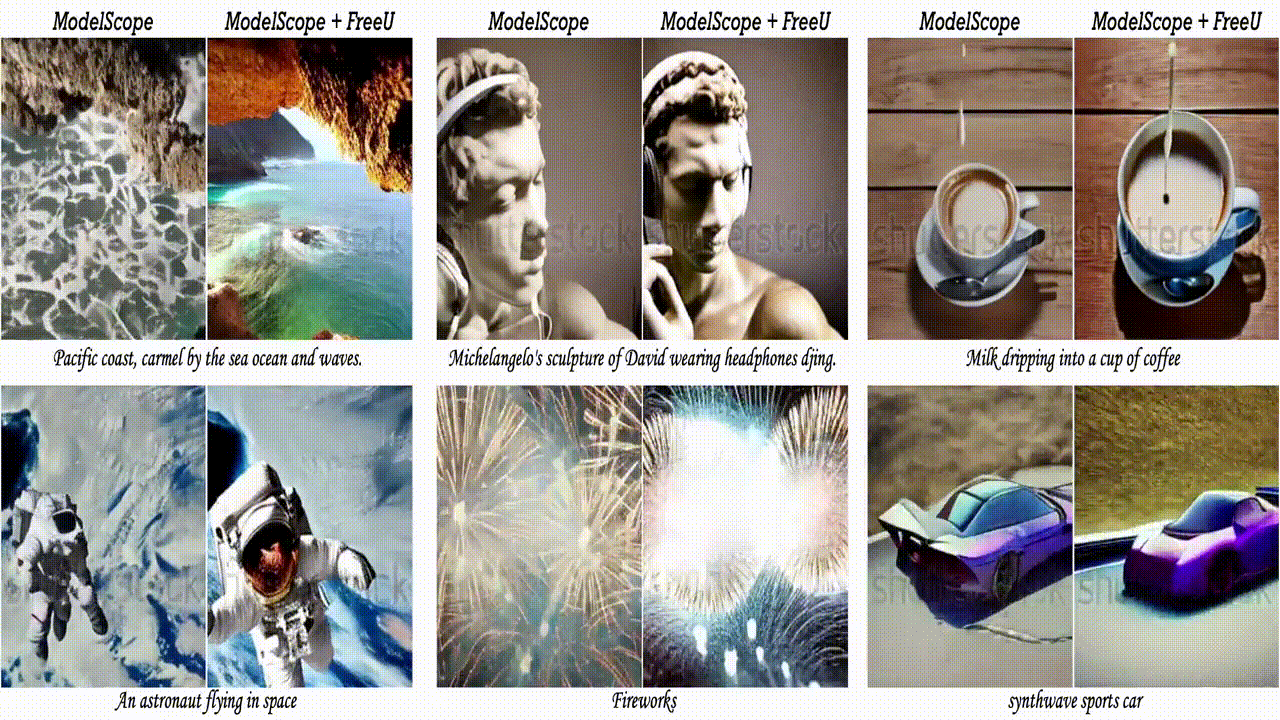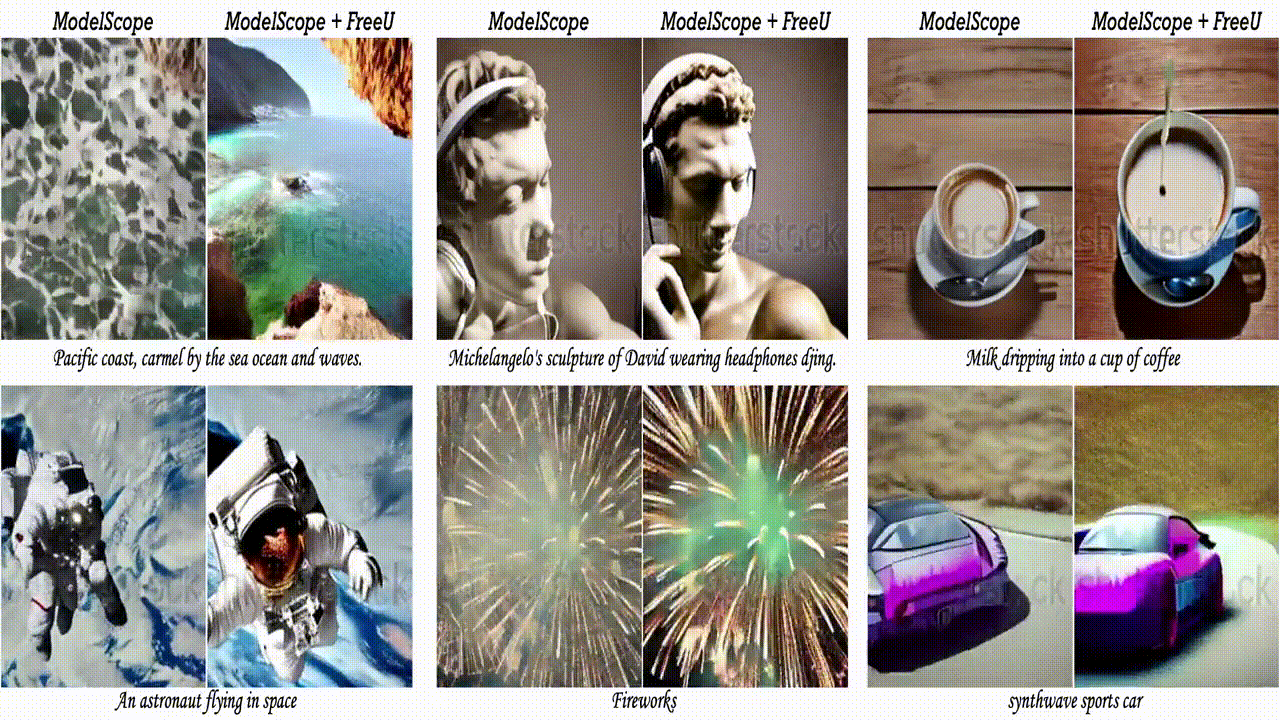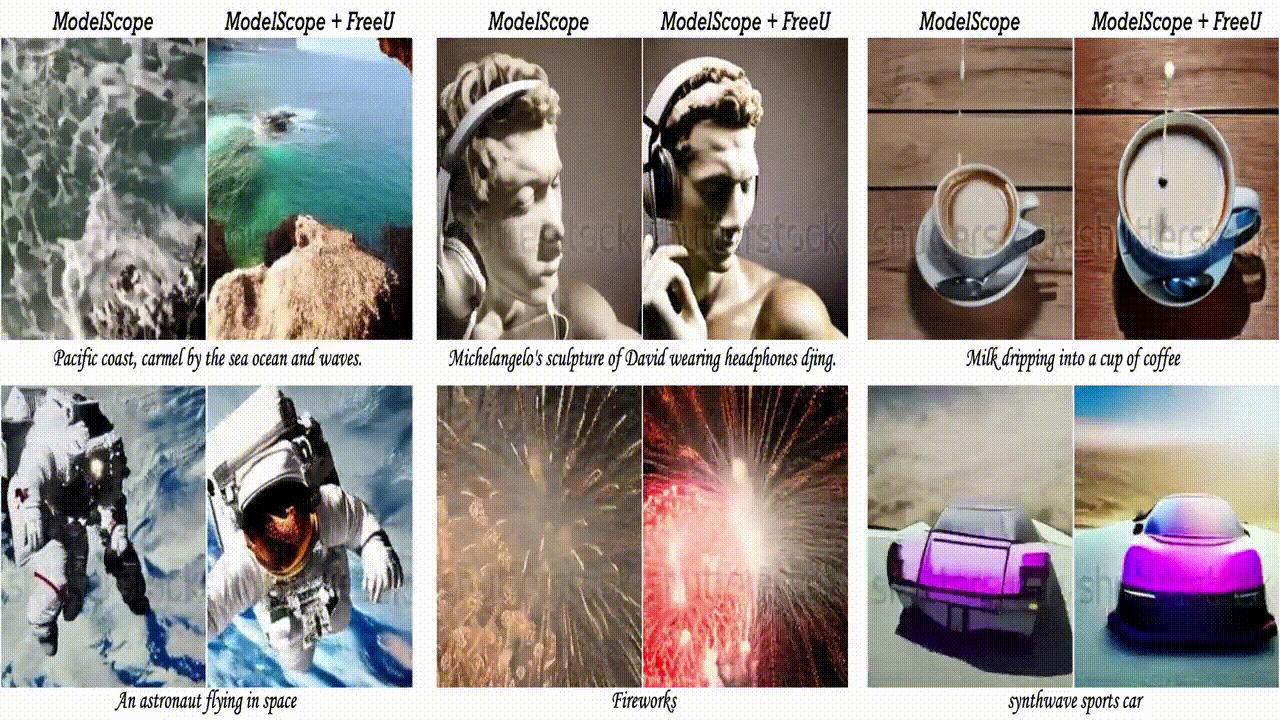
2.3. FreeU: Free Lunch in Diffusion U-Net
In this paper, we uncover the untapped potential of diffusion U-Net, which serves as a “free lunch” that substantially improves the generation quality on the fly. We initially investigate the key contributions of the U-Net architecture to the denoising process and identify that its main backbone primarily contributes to denoising, whereas its skip connections mainly introduce high-frequency features into the decoder module, causing the network to overlook the backbone semantics.
Capitalizing on this discovery, we propose a simple yet effective method “FreeU” — that enhances generation quality without additional training or finetuning. Our key insight is to strategically re-weight the contributions sourced from the U-Net’s skip connections and backbone feature maps, to leverage the strengths of both components of the U-Net architecture. Promising results on image and video generation tasks demonstrate that our FreeU can be readily integrated into existing diffusion models, e.g., Stable Diffusion, DreamBooth, ModelScope, Rerender, and ReVersion, to improve the generation quality with only a few lines of code. All you need is to adjust two scaling factors during inference.
2.4. DreamLLM: Synergistic Multimodal Comprehension and Creation
This paper presents DreamLLM, a learning framework that first achieves versatile Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) empowered with frequently overlooked synergy between multimodal comprehension and creation. DreamLLM operates on two fundamental principles. The first focuses on the generative modeling of both language and image posteriors by direct sampling in the raw multimodal space. This approach circumvents the limitations and information loss inherent to external feature extractors like CLIP, and a more thorough multimodal understanding is obtained. Second, DreamLLM fosters the generation of raw, interleaved documents, modeling both text and image contents, along with unstructured layouts. This allows DreamLLM to learn all conditional, marginal, and joint multimodal distributions effectively. As a result, DreamLLM is the first MLLM capable of generating free-form interleaved content. Comprehensive experiments highlight DreamLLM’s superior performance as a zero-shot multimodal generalist, reaping from the enhanced learning synergy.
3. 3D Computer Vision
1.3. 360 Reconstruction From a Single Image Using Space-Carved Outpainting
We introduce POP3D, a novel framework that creates a full 360-view 3D model from a single image. POP3D resolves two prominent issues that limit the single-view reconstruction. Firstly, POP3D offers substantial generalizability to arbitrary categories, a trait that previous methods struggled to achieve. Secondly, POP3D further improves reconstruction fidelity and naturalness, a crucial aspect that concurrent works fall short of.
Our approach marries the strengths of four primary components:
A monocular depth and normal predictor that serves to predict crucial geometric cues
A space carving method capable of demarcating the potentially unseen portions of the target object.
A generative model pre-trained on a large-scale image dataset that can complete unseen regions of the target
A neural implicit surface reconstruction method tailored to reconstructing objects using RGB images along with monocular geometric cues.
The combination of these components enables POP3D to readily generalize across various in-the-wild images and generate state-of-the-art reconstructions, outperforming similar works by a significant margin.
Looking to start a career in data science and AI do not know how. I offer data science mentoring sessions and long-term career mentoring:
Mentoring sessions: https://lnkd.in/dXeg3KPW
Long-term mentoring: https://lnkd.in/dtdUYBrM











Great work