Hands-On LangSmith Course[1/7]: What Is LangSmith?
Building production-ready LLM applications requires robust tools for development, monitoring, and continuous improvement. Langsmith is a comprehensive platform designed to streamline this entire process.
Offering powerful tools for detailed observability, systematic evaluation, and collaborative prompt engineering, Langsmith provides the necessary toolkit to move from prototype to production with confidence.
This article provides a tour of the platform’s core features, demonstrating how you can effectively manage and enhance your LLM applications at every stage of the development cycle.
Table of Contents:
LangSmith Core Functionality
Observability (Tracing & Monitoring) in LangSmith
Evaluation & Testing in LangSmith
Prompt Engineering & Optimization in LangSmith
Get All My Books, One Button Away With 40% Off
I have created a bundle for my books and roadmaps, so you can buy everything with just one button and for 40% less than the original price. The bundle features 8 eBooks, including:
If you have ever tried to build an application on top of a Large Language Model (LLM), then you know the struggle. When things go wrong, it’s rarely a simple bug.
Instead, you’re left trying to trace a single user interaction through a complex run tree or make sense of a sea of unstructured conversations, trying to understand why the model failed to reason correctly. Debugging its logic and figuring out how to consistently improve its performance can often feel more like an unpredictable art than a repeatable science.
Here, where LangSmith comes into action, it is designed for the entire LLM development lifecycle and reveals some fundamental principles that challenge common assumptions.
LangSmith offers essential capabilities such as observability, which includes features like automated tracing and a run tree view for debugging, identifying expensive steps, and analyzing latency bottlenecks.
Furthermore, the platform supports evaluation and experimentation, allowing users to define custom evaluators, conduct systematic testing with curated datasets, and compare experiment results side-by-side to assess the trade-offs of architectural changes.
This series will cover the following topics:
What is LangSmith? (You are here!)
Tracing with LangSmith
Playground & Prompts in LangSmith
Datasets & Evaluations in LangSmith
Annotation Queues with LangSmith
Automations & Online Evaluation with LangSmith
Dashboards in LangSmith
1. LangSmith Core Functionality
LangSmith is a commercial platform with the primary purpose of helping developers improve LLM application and agent performance at every step of the development cycle. It is designed to be a centralized platform for the entire lifecycle: building, evaluating, and monitoring.
A crucial aspect of its purpose is its adaptability: while it works well with LangChain’s open-source frameworks, LangSmith is framework agnostic, meaning it is “designed to work with any agent framework or no framework at all”.
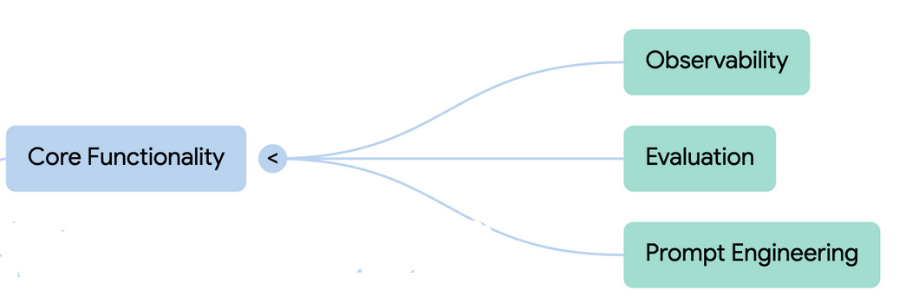
Core Functionalities of the Platform
The overall purpose of improving LLM performance is achieved through three explicit and interconnected core functionalities:
1. Observability
2. Evaluation
3. Prompt Engineering
The platform is structured to address major challenges in LLM development, particularly the difficulty in understanding how agentic applications “reason and take action”.
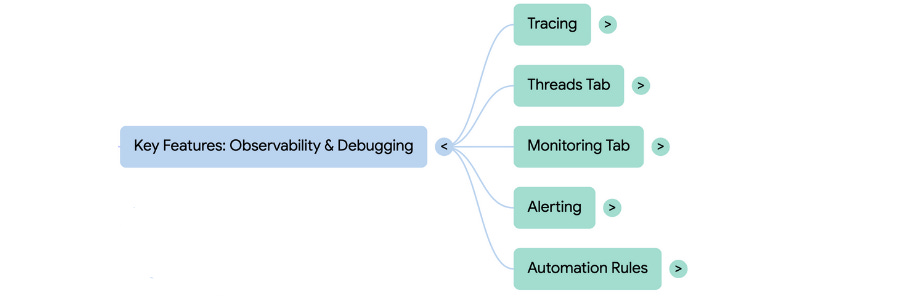
1. Observability (Tracing and Monitoring)
Observability is positioned as the fundamental starting point, driven by the belief that “great evaluations begin with great observability”.
Tracing: This mechanism “comes out of the box” and requires minimal setup (e.g., environment variables or tracing decorators). It automatically logs “each step of your application’s workflow”, allowing developers to inspect overall performance and inspect individual traces to root cause effortlessly. Tools like the run tree view assist in debugging traces and identifying “expensive steps or understand latency bottlenecks”.
Monitoring and Alerting: Observability extends to a turnkey monitoring tab that provides built-in charts on volume, success rates, and latency. LangSmith also provides alerting to proactively raise issues. Users can set up alerts (e.g., to PagerDuty or a webhook) to receive notification if “quality dips or latency spikes beyond a set threshold”. The data gathered also allows users to set up automation rules to act on the data and improve the application.
2. Evaluation (Testing and Experimentation)
Evaluation is the systematic process of testing and measurement that builds upon observable production data.
Data Curation and Auditing: The platform supports curating representative datasets through various means, including pulling from production traces, manually creating examples, or using AI to augment data. The annotation cube provides a dedicated space for auditing traces, enabling human annotators (especially those with subject matter expertise) to inspect traces, provide feedback, or add them as examples to a test suite.
Systematic Testing: LangSmith features for data sets and experimentation make it easy to “systematically test your application’s performance”. Experiments, runnable via the SDK or UI, allow both developers and non-technical stakeholders (such as product managers or business users) to participate.
Continuous Improvement: Experiments help teams continuously “measure and track your agent performance as it improves” and provide clear visibility into trade-offs (e.g., comparing improved quality versus increased latency when optimizing architecture). The platform makes it easy to compare experiments side-by-side to see which examples “regressed or improved”.
3. Prompt Engineering (Iteration and Optimization)
Prompt engineering focuses on the collaborative iteration and refinement of LLM instructions.
Optimization Tools: The Prompt Playground serves as a scratchpad for testing different models, adjusting wording, and immediately seeing the impact of changes. A side-by-side comparison view aids in analyzing variations. Additionally, the Prompt Canvas tool provides AI-optimized versions based on user feedback, aiming to make every team member a “professional prompter”.
Collaboration and Management: When an optimal prompt is developed, it can be saved in a centralized prompt library for teammates to reuse and refine. LangSmith also helps track changes over time by keeping a record of commit history.
2. Observability (Tracing & Monitoring) in LangSmith
Observability & Debugging are an essential and foundational set of key features within the LangSmith commercial platform. In the larger context, Observability & Debugging are an essential and foundational set of key features within the LangSmith commercial platform.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to To Data & Beyond to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.